##
# app/src/hello.py
from datetime import datetime
import time
def main():
# run for about 5 min: 300 sec
for i in range(60):
now = datetime.now()
dt_string = now.strftime("%d/%m/%Y %H:%M:%S")
# prepare message
msg = f"hello world at {dt_string}"
# put message to stdout and logs
print(msg)
# sleep for some seconds
time.sleep(5)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Docker - Send Container Logs to AWS CloudWatch
docker, python, logs, aws, cloudwatch

About
This post is about configuring docker container to send application logs to Amazon CloudWatch. Logs entries can be retrieved from AWS Management Console.
Environment Details
- Python = 3.8.x
- Docker version = 20.10.7
- OS = Amazon Linux 2
iamadmin:~/environment $ docker version
Client:
Version: 20.10.7
API version: 1.41
Go version: go1.15.14
Git commit: f0df350
Built: Wed Nov 17 03:05:36 2021
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Context: default
Experimental: true
Server:
Engine:
Version: 20.10.7
API version: 1.41 (minimum version 1.12)
Go version: go1.15.14
Git commit: b0f5bc3
Built: Wed Nov 17 03:06:14 2021
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: false
containerd:
Version: 1.4.6
GitCommit: d71fcd7d8303cbf684402823e425e9dd2e99285d
runc:
Version: 1.0.0
GitCommit: 84113eef6fc27af1b01b3181f31bbaf708715301
docker-init:
Version: 0.19.0
GitCommit: de40ad0
iamadmin:~/environment $ cat /etc/os-release
NAME="Amazon Linux"
VERSION="2"
ID="amzn"
ID_LIKE="centos rhel fedora"
VERSION_ID="2"
PRETTY_NAME="Amazon Linux 2"
ANSI_COLOR="0;33"
CPE_NAME="cpe:2.3:o:amazon:amazon_linux:2"
HOME_URL="https://amazonlinux.com/"Sample Application
Let us create a simple hello world application that will print “hello world” message to stdout. After each message the application sleeps for 5 seconds, and keeps on doing this for 5 mins (300 sec). After this the program exists.
Project structure of this application is
app/
└── src/
└── hello.pyWhere * app/ is the project root folder * src/ folder contain the python application code * src/hello.py is the main application
Code files are provided below
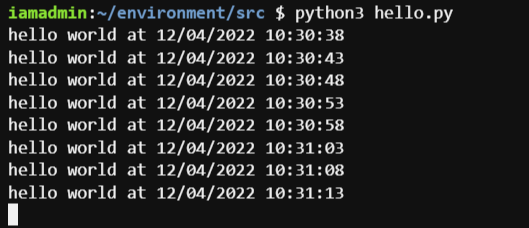
When I run the hello.py file I get the output on the termial with hello world messages like this.
Dockerize the application
Let’s put it inside a docker container. For this let’s create a Dockerfile and place it in app/ folder.
We can build our docker image by running the command from terminal at folder app/
docker build --tag python-docker .Output of this command will look like this 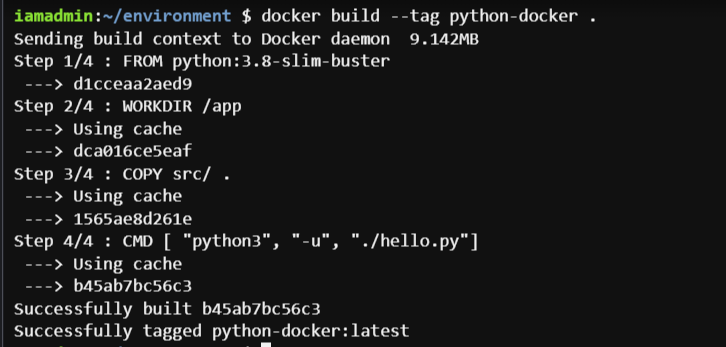
We can check the created docker image using command from terminal
docker imagesOutput of this command will look like this 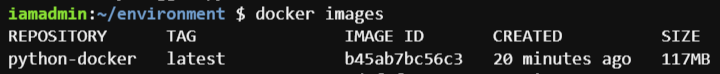
So our docker image is ready, we can now run it using command
docker run python-dockerAfter running this command you will see the application logs on the terminal. 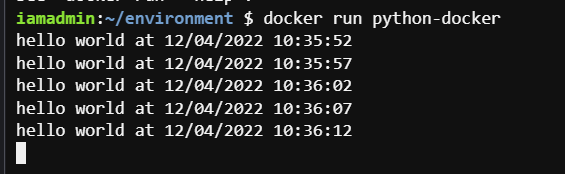
Get AWS Credentials
Now that we have our sample application and it’s docker container ready, we can work on pushing the docker logs to AWS CloudWatch. For this we need access credentials to AWS account where we want our logs to be available. We will create a separate account in AWS with CloudWatch access and use it’s credentials with docker daemon. Our steps will be * Create IAM policy with CloudWatch access * Create IAM group with that policy * Create IAM user and add that to this group
Create IAM Policy
- From AWS Console go to IAM Console
- Select Policies, and click ‘Create Policy’
- From Create Policy window, select
- Service = CloudWatch Logs
- Actions = CreateLogStream, GetLogRecord, DescribeLogGroups, DescribeLogStreams, GetLogEvents, CreateLogGroup, PutLogEvents
- Resources = All
After giving required permissions, policy summary will be like
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "DockerContainerLogs",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:GetLogRecord",
"logs:DescribeLogGroups",
"logs:DescribeLogStreams",
"logs:GetLogEvents",
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}Create IAM Group and User
- From IAM console create a new IAM group and give it some appropriate name ‘docker-logs-group’
- Attach the above created policy to that group
- From the console create a new IAM user with “Access key - Programmatic access”. Give it some appropriate name ‘docker-logs-user’
- Store access key ID and secret access key
- Add the user to the group created in last step
Configure AWS credentials for docker daemon
To configure docker daemon to use AWS access credentials, execute command from the terminal sudo systemctl edit docker. A new window will open for text to edit, and add the following lines to it. Replace my-aws-access-key and my-secret-access-key with your access keys.
[Service]
Environment="AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=my-aws-access-key"
Environment="AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=my-secret-access-key"This command will update the credentials in file /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/override.conf. Verify it using command
$ cat /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/override.conf
[Service]
Environment="AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=AKIA3VIXXJNKPUSIOR3Y"
Environment="AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=XhjlKVkZm1XdXedjgBcfLVM3FBU6zkGU"After making changes to Docker daemon we need to restart it. For this * Flush the change with command sudo systemctl daemon-reload * Restart the docker daemon with command sudo systemctl restart docker
Run docker container with awslogs driver
We can now run the docker image with awslogs driver using command
docker run \
--log-driver=awslogs \
--log-opt awslogs-region=us-east-1 \
--log-opt awslogs-group=myLogGroup \
--log-opt awslogs-create-group=true \
python-dockerlog-driverconfigures the driver to be used for logs. Default driver is ‘json-file’ andawslogsis for CloudWatchawslogs-regionspecifies the region for AWS CloudWatch logsawslogs-groupspecifies the log group for CloudWatchawslogs-create-groupspecifes that if provided log group does not exists on CloudWatch then create one
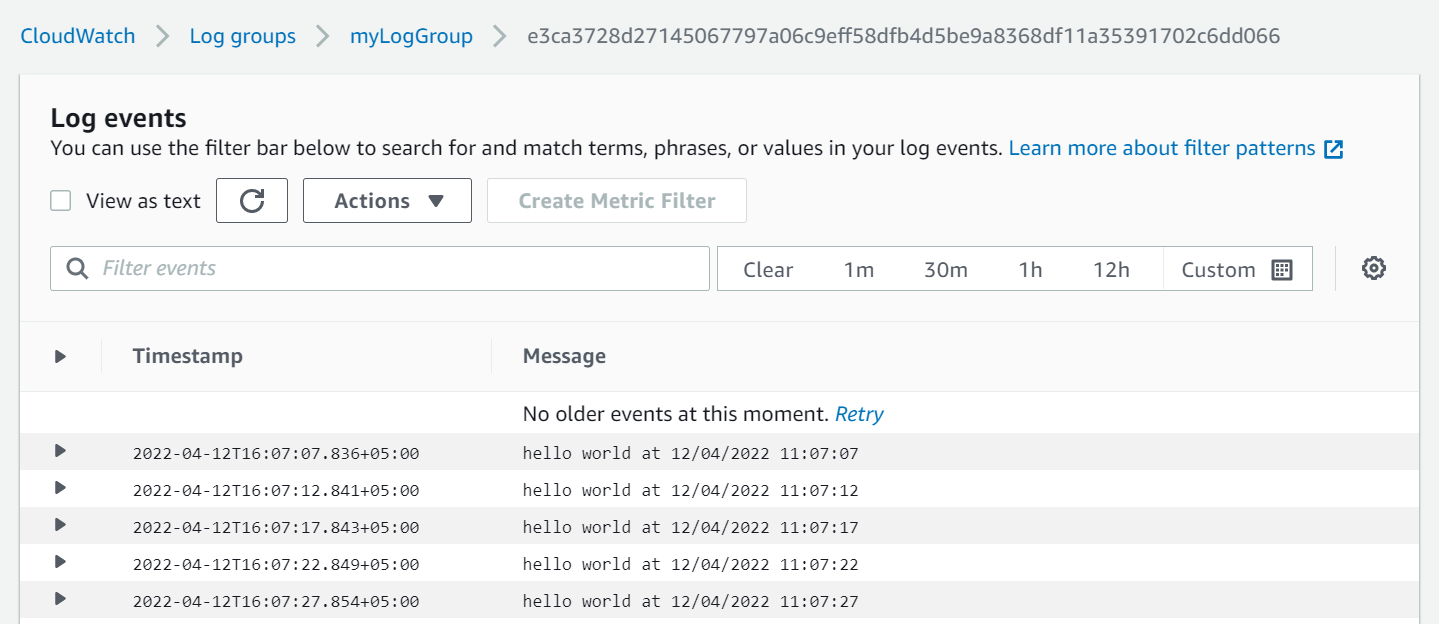
Verify Logs from CloudWatch
Go to CloudWatch console and select Log Groups and then myLogGroup. You will find the logs generated by docker container.
All the code used for this post can be obtained from the GitHub repository hassaanbinaslam/2022-04-11-docker-logs-cloudwatch
Error Messages
If docker daemon is not able to find AWS credentails then it will generate an error message similar to pasted below
docker: Error response from daemon: failed to initialize logging driver: failed to create Cloudwatch log stream: NoCredentialProviders: no valid providers in chain. Deprecated.
For verbose messaging see aws.Config.CredentialsChainVerboseErrors.If you get this message then you need to recheck the credentails passed to docker daemon.
One thing I noticed is that on Windows there is no way to pass AWS credentials to docker daemon. People have reported similar issues with docker running on MAC OS. Refer to below link for this discussion
- https://github.com/docker/for-win/issues/9684
Other method to provide AWS credentials to docker daemon
Docker documentation mentions that AWS credentails can also be set * By configuring the environment variables AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY. I have tried this approach but docker daemon is not able to pick AWS credentials from environment variables * By using AWS credentials file ~/.aws/credentials. I have also tried this approach and it does not work either
Important References
- Docker configuring logging drivers
- Amazon CloudWatch Logs logging driver
- https://transang.me/configure-docker-to-send-log-to-aws/